
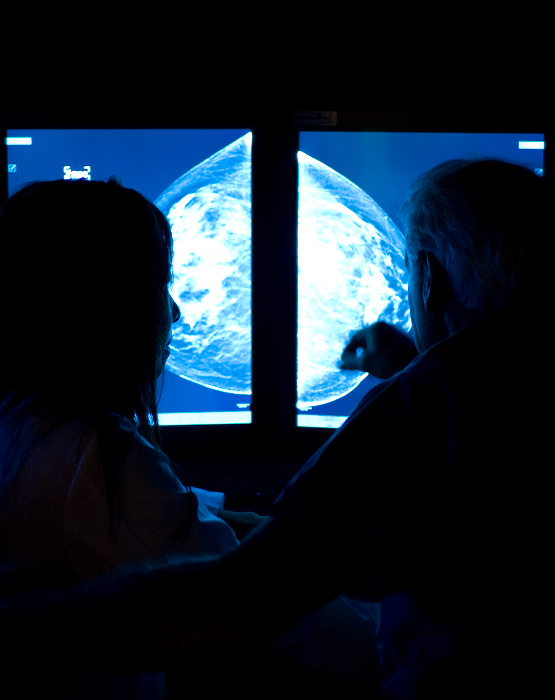
Breast Imaging
Our breast imaging radiologists are dedicated specialists who are leaders in the field. Studies have shown that specialist radiologists detect more cancers and have lower recall rates than general radiologists.
Breastlink’s state-of-the-art breast imaging technology combined with superior expertise, will provide you with the most accurate results and best patient care.
Breast Imaging Offered at All Breastlink Locations across California and Arizona including our Mobile Mammography Fleet.
Self-Requesting Mammograms
Women over 40 who are not experiencing symptoms can make an appointment for their annual screening mammogram on their own, without an order from their physician.
While a physician's order is not required, you must have an active primary care provider or OBGYN. If you do not have one, we can recommend one of our friendly providers.

Breast Imaging at Breastlink
Expert Imaging. Personalized Care
Our comprehensive breast imaging services provide high-quality diagnostics combined with superior expertise. With advanced technology and a team of expert radiologists, we deliver accurate, timely results and compassionate, patient-focused care.
What is Breast Imaging?
Breast imaging encompasses a range of advanced diagnostic procedures used by radiologists to detect, diagnose, and help prevent breast cancer. These imaging techniques play a vital role in early detection and ongoing breast health management.
Screening Mammography
A screening mammogram is a routine X-ray of the breast used to detect breast cancer in women who don't have any signs or symptoms of the disease. This is a preventative measure, recommended annually for women starting at age 40, or earlier for women considered high-risk.
Diagnostic Mammography
A diagnostic mammogram is performed when there are signs or symptoms of a potential breast issue, such as a lump, breast pain, nipple discharge, or changes found during a screening mammogram. Unlike routine screening, this specialized X-ray provides more detailed images to closely evaluate areas of concern and guide the need for further testing or treatment.
Breast Tomosynthesis (3D Mammography)
Tomosynthesis, or 3D mammography, is an advanced imaging technology that creates a three-dimensional view of the breast using X-rays. Unlike traditional 2D mammograms, which capture a single flat image, 3D mammography takes multiple images from different angles. This layered view allows radiologists to examine breast tissue in greater detail, improving the detection of subtle abnormalities, especially in women with dense breast tissue.
Breast Ultrasound
A non-invasive imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create pictures of the inside of the breast, Breast Ultrasound is used to help diagnose breast lumps or other abnormalities found that may be detected on a mammogram. Breast Ultrasound is used in conjunction with Mammography.
Enhanced Breast Cancer Detection (EBCD)
EBCD uses artificial intelligence (AI) to help our specialty trained breast radiologists detect even subtle lesions by pointing out areas of suspicion that are not always visible to the human eye.
Breast MRI
Breast MRI is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves—not X-rays or radiation—to produce highly detailed images of breast tissue. It is often used alongside mammography or ultrasound to provide additional information for breast cancer screening, diagnosis, or treatment planning.
If a breast lesion has been detected, a breast biopsy may be required to determine its cause.
What is a Breast Biopsy?
A breast biopsy is a medical procedure that extracts a tiny sample of breast tissue from the body for the purpose of testing. A breast biopsy may be performed in women who have detected a lump during physical examination, or in women whose screening mammography revealed a potential lesion. There are several different types of breast biopsy.
Why are Breast Biopsies Performed?
Breast imaging procedures help patients and their physicians detect potential abnormalities in breast tissue. Breast imaging procedures can also help physicians rule out cancer in some women who have detected a potential abnormality. However, a breast biopsy is required for physicians to make a conclusive breast cancer diagnosis.
Different types of breast biopsies are performed for different reasons. If a woman’s physician recommends a biopsy, she should ask why.
What to Expect From a Breast Biopsy
Breast biopsy experiences will vary based on the type of biopsy being performed. Image-guided biopsies use medical imaging technologies during the process to help physicians locate problem areas. The type of breast biopsy a physician recommends will depend on a patient’s specific circumstances, such as the location and size of a lesion in her breast.
The different types of breast biopsy include:
Fine Needle Aspiration Breast Biopsy
In a fine needle aspiration breast biopsy procedure, an extremely thin needle attached to a syringe is used to extract a small amount of cells from a woman’s breast tissue. Fine needle aspiration biopsy is an effective method for distinguishing solid masses from fluid-filled cysts. It can also be used to drain a painful benign cyst, if a patient desires.
Core Needle Breast Biopsy
Core needle biopsy uses a thin, hollow needle to extract tissue samples from the breast tissue. Prior to core needle biopsy, anesthesia will be injected into the target area. This numbs the breast of the woman being biopsied to prevent pain, but allows her to remain awake and alert during the procedure. Between two and six samples are extracted and each is approximately the size of a grain of rice.
Stereotactic Breast Biopsy
Stereotactic biopsy uses mammography during core biopsy to help a radiologist determine the exact location of the concern within a breast to be biopsied.
Ultrasound-guided Breast Biopsy
Ultrasound may be used during fine needle aspiration biopsy or core needle biopsy to help a radiologist determine the exact location of the mass within a breast to be examined.
MRI-guided Breast Biopsy
MRI may be used during a core biopsy to help a radiologist determine the exact location of the mass within a breast to be biopsied. This is used for concerns seen only on a MRI.
Surgical Breast Biopsy
If physicians are unable to determine the exact nature of a breast abnormality using needle biopsy, surgical biopsy may be required. There are two types of surgical biopsies: incisional and excisional.
During incisional biopsy, surgeons remove just enough of a suspicious area to make a diagnosis. During excisional biopsy, surgeons attempt to remove all of the suspicious area. Surgical biopsies require either local or general anesthesia, often require stitches and may cause scarring.
Breast Imaging @Breastlink


3D Mammography with Dr. Jason McKellop

Put the Power of Artificial Intelligence Behind Your Mammogram!
At Breastlink, we are transforming breast cancer detection with a revolutionary offering called Enhanced Breast Cancer Detection (EBCD). EBCD is the only solution of its kind—a package of breast care tools that work in concert to optimize your annual breast cancer screening exam. If you want greater confidence in your results, schedule your screening mammogram appointment today and say YES to EBCD!
LEARN MORE

